Environmental Research: Available online 14 May 2022, 113433
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113433
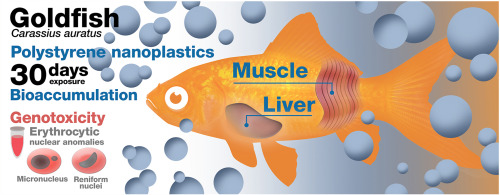
Abstract
The extent of the widespread, planetary contamination by plastic waste is difficult to fully capture. Nanoplastics (NPs) are currently in the center of research concerning plastic litter, both for the analytical challenges they pose and for their potential to provoke hazardous effects in organisms. However, there are still many unanswered questions in this multidisciplinary field, with a crucial missing piece being the quantification of NPs in fish tissues after in vivo exposures. Another relevant question that is still greatly unexplored is how a chronic exposure to NPs will affect fish health. This study aims to provide answers to both of these relevant knowledge gaps. To this end, goldfish (Carassius auratus) were exposed to 44 nm polystyrene (PS)-NPs via water for 30 days. Following the exposure, gastrointestinal tract, liver and muscle were sampled for PS-NPs analysis by means of size exclusion chromatography coupled to high resolution mass spectrometry. PS-NPs were detected in all liver and muscle samples of exposed fish, with higher concentrations in liver than in muscle, whereas no PS-NPs were detected in the gastrointestinal tract. Nevertheless, exposure to PS-NPs did not induce changes in hematology parameters nor in cortisol and glucose levels in plasma. On the other hand, even a relatively low concentration of PS-NPs was able to cause DNA damage, measured by an increase in erythrocyte nuclear abnormalities, suggesting that PS-NPs can reach the cell nucleus and cause genotoxicity. These results show for the first time that PS-NPs find their way to fish muscle after chronic exposure, where they bioaccumulate, but do not alter fish survival nor hematological or physiological stress indicators. The accumulation of PS-NPs in fish muscle can represent a threat to human health as a possible route of exposure to small-sized plastics. The present results in a model fish species open windows for future studies in edible fish species.
